About Zero Trust 
"Never implicitly trust, always and continuously verify"
Zero Trust is a relatively new security paradigm which goes beyond the traditional defense-in-depth perimeter-based strategy and treats all communications and resource requests as initially untrusted and requiring continuous verification before access to those resources is granted. One of the greatest benefits of Zero Trust is that it can eliminate lateral movement from a compromised system within a network.
The recent Executive Order on Improving the Nation's Cybersecurity defines "the term “Zero Trust Architecture” [to mean] a security model, a set of system design principles, and a coordinated cybersecurity and system management strategy based on an acknowledgement that threats exist both inside and outside traditional network boundaries. The Zero Trust security model eliminates implicit trust in any one element, node, or service and instead requires continuous verification of the operational picture via real-time information from multiple sources to determine access and other system responses. In essence, a Zero Trust Architecture allows users full access but only to the bare minimum they need to perform their jobs. If a device is compromised, zero trust can ensure that the damage is contained. The Zero Trust Architecture security model assumes that a breach is inevitable or has likely already occurred, so it constantly limits access to only what is needed and looks for anomalous or malicious activity. Zero Trust Architecture embeds comprehensive security monitoring; granular risk-based access controls; and system security automation in a coordinated manner throughout all aspects of the infrastructure in order to focus on protecting data in real-time within a dynamic threat environment. This data-centric security model allows the concept of least-privileged access to be applied for every access decision, where the answers to the questions of who, what, when, where, and how are critical for appropriately allowing or denying access to resources based on the combination of sever[al criteria]."
The views of Zero Trust embodied in the Zero Trust Maturity Model which is assessed within this application adhere to the Executive Order's definition and are primarily derived from the Zero Trust eXtended (ZTX) model developed by Forrester. In this model of Zero Trust, the foundation is built upon a robust understanding of the environment that the organization operates in and that the organization is at least doing the basics as it relates to cybersecurity (e.g, the CIS top 18 (formerly the SANS top 20)). Then, the 7 domains of Zero Trust are built upon that foundation. Those domains are: Users (a/k/a people or identity), Endpoints (a/k/a devices), Data, Networks, Workloads (a/k/a applications), Visibility & Analytics, and Automation & Orchestration. The outcome of moving towards Zero Trust is increased Governance (as well as reduced risk, improved user experience, lower costs, speedier & more reliable software development, and a variety of other positive outcomes).
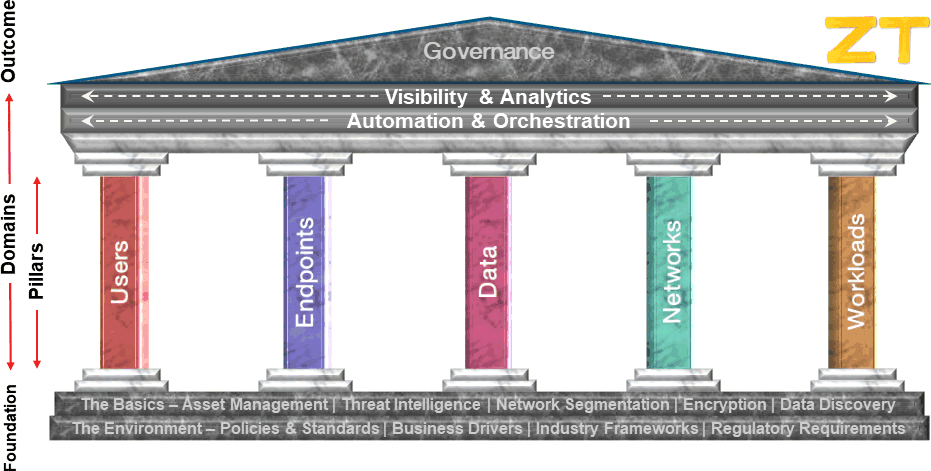 |
It is these 7 domains as well as The Basics that are the inspiration behind the assessment criteria in the Zero Trust Maturity Model utilized here.
Following are some links to various podcasts, presentations, and panel discussions which discuss this point of view on Zero Trust as well as the Zero Trust Maturity Model:
|